
How about some green tea facts?
Tea is the most popular drink after water. People all over the world consume it. So, what are the advantages of green tea? And, what are the nutrition facts?
Green tea is low in caffeine. It has an average of 15 – 25 mg of caffeine (per gram of tea).
To compare, black tea contains 40 – 70 mg of caffeine. A tall cafe latte (354 ml) from Starbucks has 75 mg of caffeine. A tall Starbucks brewed coffee has 260 mg of caffeine. And, a can of Coca-Cola (354 ml) has 32 mg of caffeine.
Green tea has a high amount of the catechin epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG). It has 2 – 3 times more than black tea. Green tea has an average of 80 mg of EGCG (studies vary from 2.31 mg – 203.20 mg) for every gram of tea.
Decaf green tea only has about 26 mg of EGCG. Black tea has about 9 mg. And Oolong tea has around 35 mg.
Generally, bottled tea has a lower amount of catechins than brewed tea.
Some green tea bags contain around half the amount of EGCG as loose leaf green tea. However, hotter water and a longer brewing time can increase the level of EGCG.
It is better to use triangular or pyramid-shaped teabags that are large enough to hold larger tea leaves. Using these tea bags has almost the same benefits as regular loose leaf tea.
The catechins and L-Theanine (γ-glutamylethylamide) promote the feeling of relaxation. The catechins affect the central nervous system and allow the body to calm down.
L-Theanine is an amino acid that is found in green tea and black tea. L-Theanine has been shown to reduce stress and offset the effects of caffeine. Read more green tea facts about hypertension.
Yes. Scientists have discovered that green tea has anti-cancer, anti-oxidant, anti-microbial, and anti-inflammatory properties.
Topical green tea might be able to protect the epidermis. EGCG, the key ingredient in green tea, promotes cell differentiation, which repairs the skin.
Most of the research has involved fresh green tea opposed to commercial premade products. So, some products on the market may not contain the full benefits of green tea because of oxidation.
Research is currently being done on lipid-soluble tea polyphenols, which prevent the green tea from oxidizing and have similar results as fresh green tea. Read more green tea facts about skin care.
It is possible to drink too much green tea if you are sensitive to caffeine or have anemia.
Pregnant and breast-feeding women should drink no more than 1–2 8 oz glasses a day.
Green tea catechins can cause a decrease in the absorption of iron from food. If you have low iron, it is best to add lemon to your green tea to increase iron absorption, or consume tea between meals. Read more green tea facts about side effects.
Cabrera, C., Artacho, R., & Giménez, R. (2006). Beneficial effects of green tea – A review.Journal of the American College of Nutrition, 25(2), 79-99.
Cooper, R., Morré, D., & Morré, D. (2005). Medicinal benefits of green tea: Part I. Review of noncancer health benefits. Journal Of Alternative & Complementary Medicine, 11(3), 521-528.
Jamieson, M., & McKinley, H. (2009). Handbook of Green Tea and Health Research. Nova Science Publishers.
USDA Database for the Flavonoid Content of Selected Foods, Release 2.1. (2007). Retrieved from http://www.ars.usda.gov/services/docs.htm?docid=6231
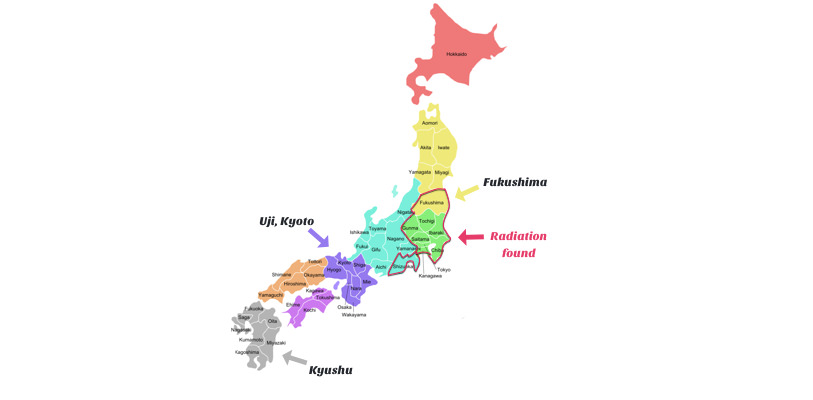
Japanese tea and radiation is a delicate topic. There are strong opinions on both sides of the fence. Find out why I’m not worried about radiation in Japanese tea.

Choose the best green tea bottled tea from our list ranking 8 popular brands. Now you can compare the facts and decide which brand you want to drink.

Do you know where your green tea comes from? Find out how Chinese green tea and Japanese green tea are different, such as taste, antioxidants, and lead.

Green Tea Powders are not all created equal. Find out what the differences are and where to get the best Matcha green tea powder!

Feel confident choosing green tea vs black tea when you compare caffeine, antioxidants, and vitamin C.

Grasp the basic concepts of harvesting and processing green tea plants. Find out what classifies green teas as sencha, gyokuro, tencha, or matcha.

Know which tea bags are better than others. Find out how much EGCG, catechin, and caffeine is in your green tea bag. Learn a few steeping tricks to get more catechins.

Find out how tea companies are using maltodextrin as a filler in green tea mixes, why you should be worried, and what products to avoid. Ask questions about what’s in your tea.

Don’t know what to do with your raw tea leaves? Make your own green tea using the traditional Japanese tea processing method or the modern-day microwave method.

Find out how to choose the best loose leaf green tea to get the most catechins. Stay away from overly processed teas such as tea bags and decaffeinated brands.

How safe is your tea? If it comes from China, you may be getting more than you asked for. Read the shocking truth about pesticides in green tea.

What is EGCG? Find out why it is important to you, the best way to get it and how much is too much! Turns out green tea may be your best source!

Are you concerned about lead in your tea? Find out how to protect yourself and how to reduce your green tea lead consumption.

The amount of EGCG in loose leaf green tea depends on many factors such as age of leaves and preparation. Find out how you can choose the best green tea.